Integrated Risk Management
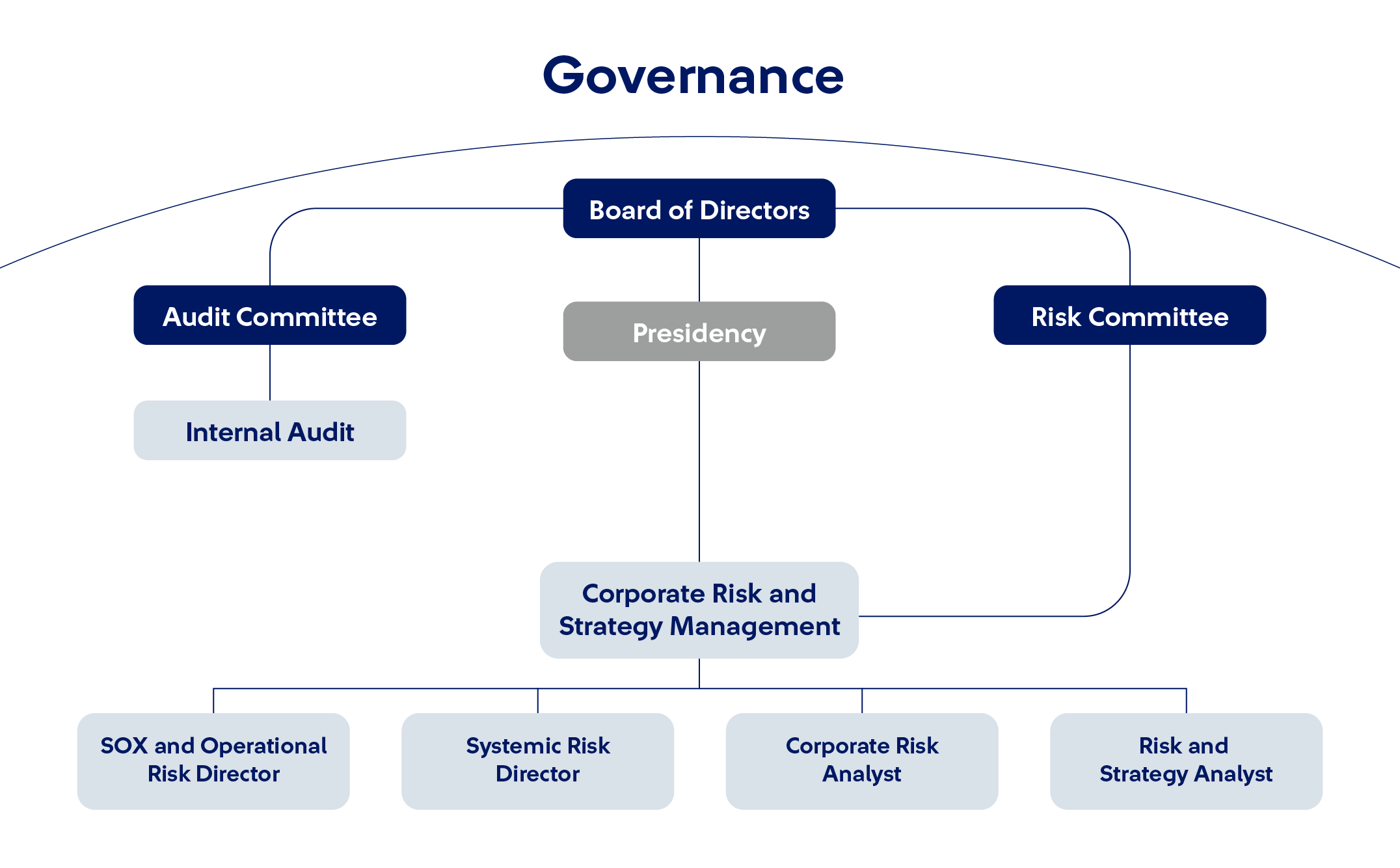
Lines of defense
The company's risk management objective is to achieve effective treatment of exposures and their severity level, considering the financial goals of the business, overall risk appetite, and external legal constraints.
The company follows a "Three Lines of Assurance" model, where each line has a clearly defined organization, responsibilities, and functions to ensure the effective implementation of risk management mechanisms. These three lines include the operational areas that execute processes, the Risk and Compliance areas responsible for prevention and monitoring, and the Internal Audit department, which independently evaluates risk management.
Additionally, the Company engages independent consultants to conduct external audits of processes identified as critical or highly relevant, based on quantitative modeling and qualitative analysis. This practice contributes to strengthening the internal control system and the risk management process.
It is composed of the areas that carry out processes in the Company. lts
performance is based on self-control, and its responsibilities include identifying
and managing risks, as well as reporting them if necessary.
It is composed by the Risk and Compliance areas, its responsibilities are related
to prevention, supporting the first line, and defining guidelines.
It is the Internal Audit department, which independently assesses risk
management.
Risk Management Process
To establish the risk management standards for Grupo SURA and ensure that it is comprehensive and effective, a Risk Management Framework (RMF) has been implemented. Grupo SURA, in its capacity as Holding Company, is responsible for ensuring compliance with this policy throughout the Financial Conglomerate, considering the scope and variability in the capacity to control its subsidiaries and associates. The RMF provides guidelines and mechanisms for strategic risk management in all subsidiaries and associates and defines the responsibility for the entities that make up the Financial Conglomerate to establish their own risk management systems, following the guidelines of the RMF. In addition, Grupo SURA may intervene to support risk management in situations that may affect the Financial Conglomerate.
Likewise, all employees will be responsible for managing the risks arising from their functions, establishing the relevant control mechanisms and, together with the process leaders, keeping their risk matrices up to date. In addition, they must inform Corporate Risk Management in the event of significant changes in risks, controls or the materialization of events.
Risk management at Grupo SURA is focused on two fundamental objectives:
Generate timely information that reveals the degree of exposure of the company to factors that may represent both significant opportunities and threats to its sustainability and that of the Financial Conglomerate.
Measure and model the phenomena associated with each identified factor to anticipate impacts in Grupo SURA’s search for sustainable profitability as an investment manager.
This process focuses on both the internal risks inherent to its business model, including those linked to people, systems and processes, as well as the risks related to the financial conglomerate. For the management of internal risks, there is a system that includes policies, own methodologies, the management of senior management and the collaboration of process leaders. In addition, in its role as a holding company, Grupo SURA assumes responsibility for managing the risks affecting the Financial Conglomerate, paying special attention to systemic factors and their influence on the overall sustainability of the portfolio. The company is also actively involved in overseeing its investments by serving on Boards of Directors and Committees, as well as providing regular reports on investment performance and playing a key role in the corporate arena.
To carry out the process, Grupo SURA has a generic methodology for managing risks. It is important to remember that considering the variations that exist between the different types of risks, variations may occur in these stages, which are specified in the Risk Management Manual, previously mentioned.
Contextualization: Analysis of the issue to be evaluated, identification of possible risks and their evolution in the Company.
Identification: A list of possible risks and their causes, regardless of whether they are under the Company’s control.
Analysis and evaluation: Assess the likelihood and impact of risk, considering causes and consequences.
Management: Define the treatment of risk, including acceptance, transfer, treatment, prioritization or avoidance, with action plans and responsible parties.
Monitoring and reporting: Regularly monitor risk and adjust action plans as needed.
Given that each type of risk has its own definitions, nature and scope, Grupo SURA has developed specific manuals detailing the methodologies adopted for its management. The following section provides a description of each risk type, whose exposure and level are assessed on a quarterly basis. The results of this analysis are communicated internally to senior management through the Board of Directors, and publicly through the Quarterly Report—when relevant changes or material events are identified—and the Annual Report, available on the Company’s website.
Risk Appetite Framework – Grupo SURA
Grupo SURA has established a formal and structured Risk Appetite Framework (RAF) that defines the type and level of risk the organization is willing to assume in pursuit of its strategic and financial objectives. This framework is led by the Risk Management area and approved by the Board of Directors. It is designed to be dynamic and adaptive, evolving as the organization deepens its understanding of the specific risks of the Financial Conglomerate and as environmental conditions change. The RAF sets the principles, governance structure, and analytical tools that guide risk-based decision-making at the Holding, without replacing the individual risk management frameworks of its subsidiaries.
The process begins with the identification of strategic, financial, operational, and external risks relevant to Grupo SURA as an investment manager in Latin America. These risks are assessed both qualitatively and quantitatively to determine the current level of exposure. Based on this, the Risk area develops a risk appetite proposal for the Holding, which defines the maximum aggregate level of exposure considered acceptable. This proposal is structured through defined indicators for each risk, complemented by associated risk levels: threshold (a reference point or early-warning signal indicating proximity to the appetite limit), appetite (the desired level of risk exposure the organization is willing to assume), tolerance (acceptable short-term deviations from appetite), capacity (the absolute maximum level of risk exposure). For each level, the RAF establishes the actions that must be taken to ensure that each identified risk is managed within the limits approved by the Board of Directors.
The RAF not only defines limits to contain potential threats to financial stability, reputation, or operational continuity, but also aims to generate useful information that supports strategic decision-making and fosters long-term value creation. It explicitly recognizes the systemic interdependencies within the conglomerate’s investment portfolio, as well as the fact that certain risks cannot always be avoided but must be managed through informed decisions. This framework is integrated with capital allocation and strategic planning processes, ensuring alignment between the risks assumed and long-term value generation.
Once defined, the risk appetite proposal is submitted to the Board of Directors for review, adjustment if necessary, and formal approval. Additionally, ongoing monitoring of risk exposures is conducted through key risk indicators, which are reported periodically to the executive team and at least quarterly to the Risk Committee and the Board of Directors. These indicators enable Grupo SURA to maintain an up-to-date risk profile, detect deviations from defined appetite levels, and trigger timely corrective actions.
Risk Management Culture in the Business Group
At Grupo SURA and its portfolio companies, the risk management culture is promoted across the entire Business Group. This approach is supported by a set of integrated strategies that include continuous training, alignment of financial incentives, and the systematic incorporation of risk criteria into business processes. The main pillars of this culture are outlined below:
1. Specialized Risk Management Training at All Levels
– Training and awareness programs are delivered to members of governance bodies and other strategic forums. These sessions cover key topics such as corporate governance, regulatory compliance, enterprise risk management, and fiduciary responsibility, with the goal of strengthening their role in overseeing risk appetite and making informed decisions regarding organizational exposure.
– The Business Group offers risk training programs to all employees, emphasizing topics such as risk management, operational risk, fraud, business continuity, information security, and remediation plans. At SURA Asset Management, the program “Tus acciones marcan el camino” promotes shared responsibility and a preventive approach in identifying, reporting, and addressing risk events. Meanwhile, Suramericana has consolidated its training platform “Vivir el Aprendizaje”, which includes mandatory certifications in areas such as information security, ethics and corporate governance, SCIRF–SOX, and IFRS, among others. These initiatives help build capabilities to manage the most relevant and cross-cutting risks throughout the organization, regardless of role or level.
2. Integration of Risk Criteria into Products and Services
Risk criteria—including those related to risk appetite and ESG factors—are structurally incorporated into the design and evaluation of products, solutions, and new business ventures, particularly in sectors classified as critical or outside risk appetite. This integration is aligned with corporate guidelines that prioritize sustainability, risk-adjusted profitability, and the preventive management of potential impacts.
3. Financial Incentives Aligned with Risk Management
Risk management is embedded within the variable compensation models across the portfolio companies. Performance evaluations include indicators linked to risk appetite compliance and risk management maturity in key areas such as market, credit, liquidity, ALM, and operational risk. This alignment ensures that financial outcomes go hand in hand with prudent and sustainable risk management.
Systemic risks
It refers to the probability that an event or series of events may compromise the proper functioning and stability of a system; in the case of Grupo SURA, the one or those related to the financial system. This risk is usually associated with participants who have a high degree of interconnectedness or share material exposures to common risk factors, derived from their economic activities or external sources, such as the economic, political, social, regulatory, environmental and technological environment of the territories where they operate.
This is the one that arises from exposures whose potential for loss is borne by the Companies of the SURA Business Group, and which is significant enough to compromise the solvency or general sustainability of the entities that make it up. Such exposures may be caused by risk factors associated with counterparty events, credit, investment, insurance, market, other risks, or a combination or interaction thereof. This type of risk arises when its source is the same and, therefore, its effect is immediately manifest in the Company(s) sharing such exposure.
It is the result of the concatenation of situations generated by the materialization of a specific event (financial, operational, reputational, business, or a combination of these) that occurs in any of the Companies of the SURA Business Group, the economic sector or territory where they operate; based on the existing interconnections, it allows the propagation of risk in different forms. which leads to an affectation in which a material portion of the set of Companies is involved.
Threats and opportunities that may manifest themselves on Grupo Sura’s investment portfolio because of the effects generated by sources external to its operation from the different dimensions that make up the environment of the territories where it operates.
Strategic risks
These are derived from internal and external events and trends that may generate a deviation from the trajectory of value generation and impact the sustainability of the Company.
Refers to the external opportunities and threats that originate in the dimensions of the environment in which the Company operates, specifically, the economic, social, political, regulatory and environmental dimensions.
Associated with the need to have people who have the knowledge and skills required to comply with the strategy, with the ability to adapt and react in a timely manner to changes in the environment, and with an adequate level of understanding and commitment to the Company’s strategic definitions.
The perception of the various stakeholders with whom the Company interacts represents a fundamental asset for the fulfillment of strategic objectives. A situation of disrepute, bad image, negative publicity, among others, whether true or not, with respect to the Company and its business practices, could have effects on relations with stakeholders.
Possible situations or challenges that may arise due to the Company’s governance structure. By properly managing these risks, Grupo SURA can promote greater investor confidence, ensure fairness and accountability, and strengthen its reputation in the market and generate a more solid and sustainable environment for its success and growth.
Refers to the challenges associated with investing and financing through capital markets. They relate to external factors, such as changes in economic, political, and regulatory conditions; By properly managing these risks, the Company can protect its investments and expand its financing alternatives in the capital markets environment.
Financial risks
It refers to variations that affect the Company's results, derived from changes in market conditions, asset prices or non-compliance with its own obligations or those that third parties have with the Company.
Refers to the Company’s ability to generate the resources that allow it to meet its obligations to stakeholders and to properly operate its businesses.
The management of this risk seeks to reduce the probability of incurring losses derived from the non-compliance of financial obligations contracted by third parties with the Company.
The management of this risk seeks to mitigate the impact of market price variations on the value of the portfolios managed and the Company’s revenues.
This refers to the financial and capital capacity of an entity to cover its unexpected risks, based on its ownership structure and the exposures that arise from its business.
Operational risks
These are those that, due to internal or external events, directly affect the Company's operation and, with it, its results. In the case of internal events, they correspond to those that derive from the operation of the Organization and that are associated with people, technology, processes and information. External events are those beyond the Company's control, such as the materialization of natural hazards or cyberattacks, among others.
These refer to events that prevent the Company’s economic reality from being adequately reflected in the financial statements that are disclosed to its different stakeholders.
These are defined as the set of individual and/or collective behaviors of employees and other stakeholders that are not aligned with the frameworks of action declared or promoted by the Company and with current regulations.
These are those that may generate an interruption of business functions due to the unavailability of key personnel, critical technology services and/or impossibility of access to the Company’s physical facilities.
These are related to the effects derived from the uncertainty associated with having information, processes or devices exposed in cyberspace and the interactions that are generated there.
Emerging Risks and Trends
Risk management in the financial industry is undergoing significant changes due to increasing regulatory requirements globally, the rapid advancement of emerging technologies, and the growing threat of climate change. In anticipation of this trend, the Company constantly monitors emerging risks and establishes plans and actions to further improve the efficiency and effectiveness of risk control. Grupo SURA has been monitoring risks such as climate change, erosion of social cohesion, extra-longevity, growth of the middle class and the evolution of FinTech as a priority. Any significant changes related to these risks will be communicated in the annual report and should a material threat be identified at any time, this update will be included in the corresponding quarterly report.
Investor Kit Q425
Download our investor kit, a tool that will allow you to easily utilize the figures of our organization.
Download Here